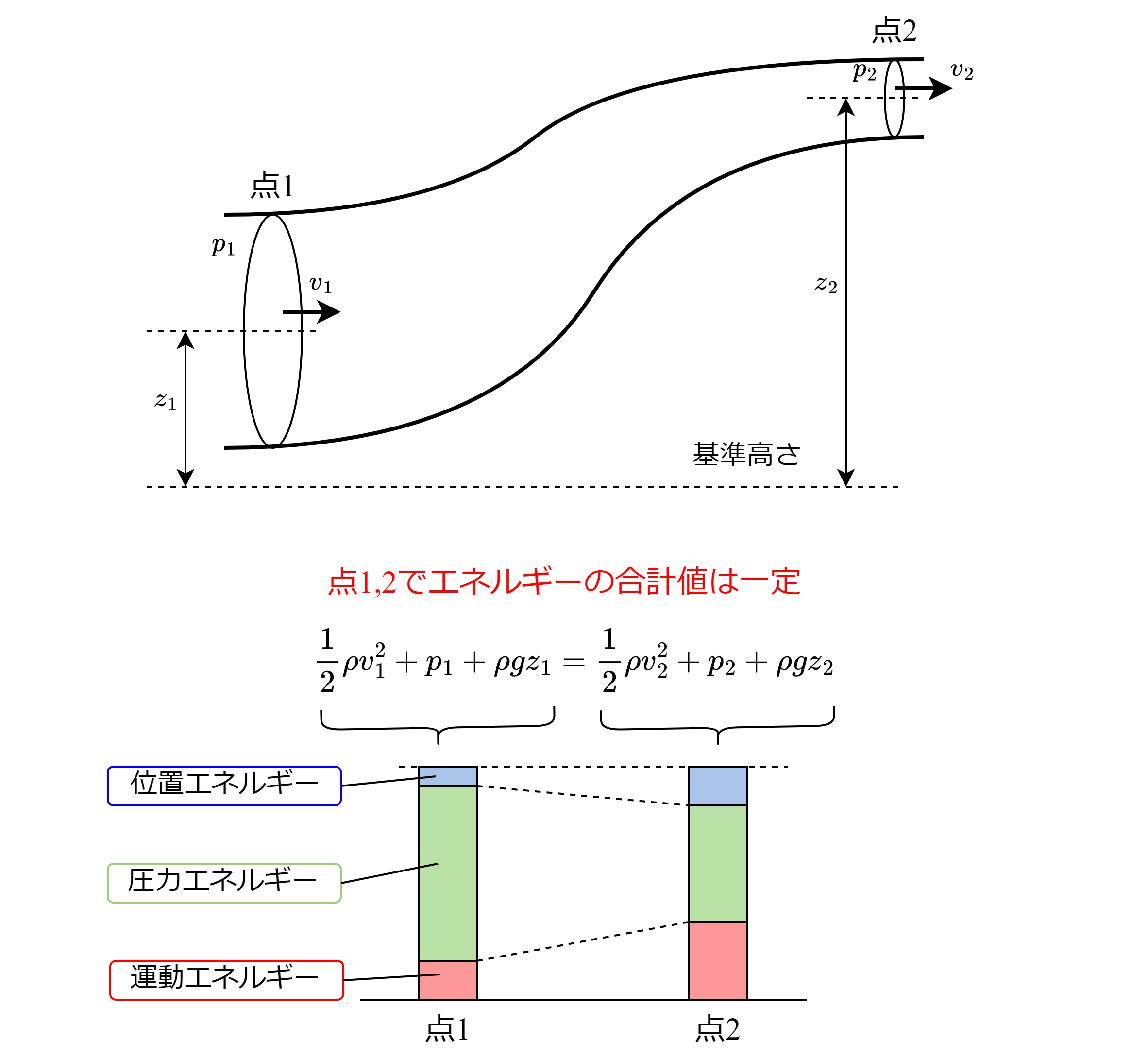
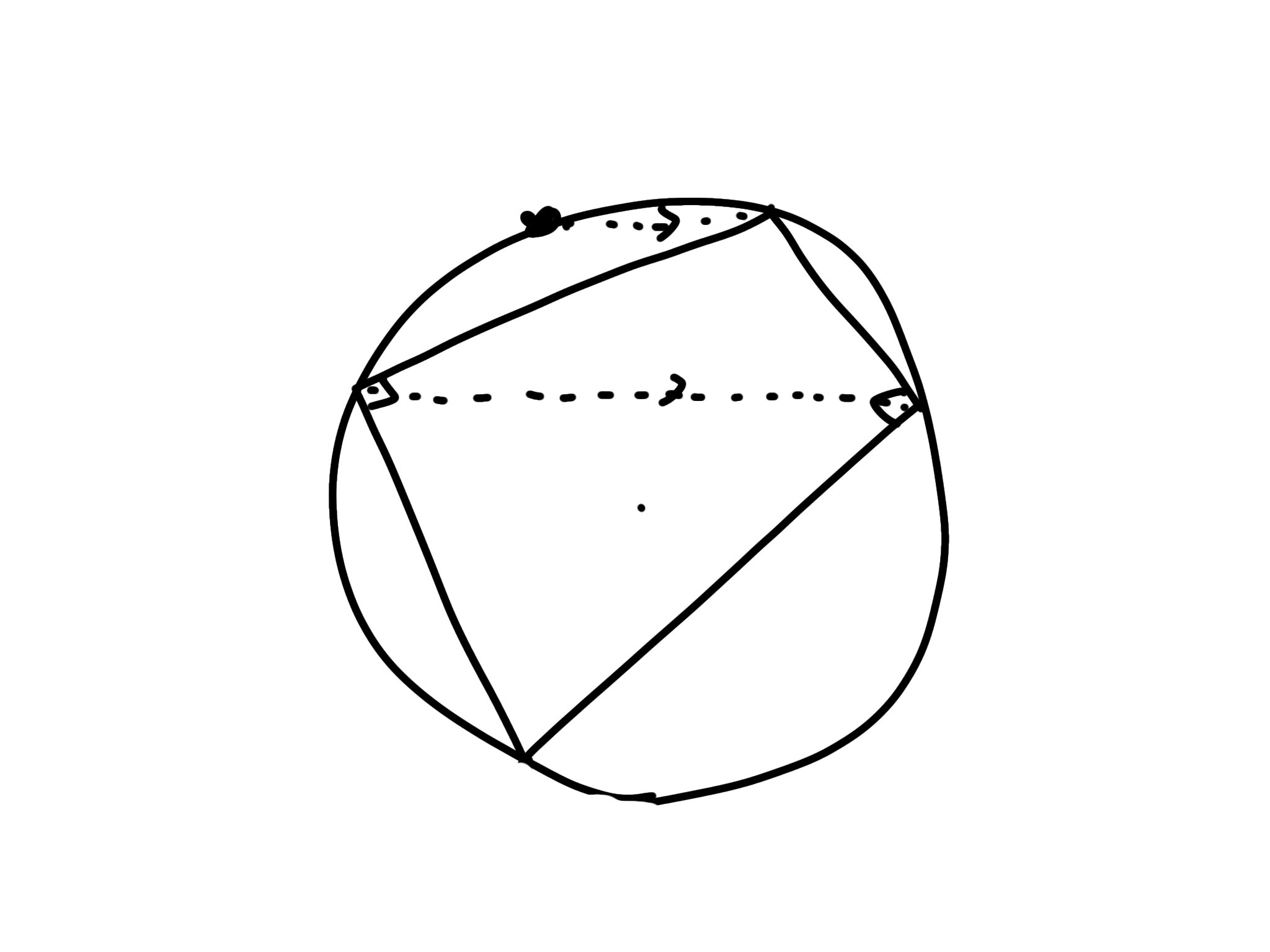
ユークリッド幾何学において、ボッテマの定理(ぼってまのていり、英語: Bottema's theorem)とはオランダの数学者オーネ・ボッテマ(フローニンゲン, 1901–1992)にちなんで名づけられた定理である。
三角形 についてそれぞれ ,を一辺とする正方形を外側に描く。このときそれぞれの正方形の、と反対の点を結んだ線分の中点はの位置に依らない。
または、辺の中点をとしを満たす三角形の内側の点、つまりを満たす点となる。
ボッテマの定理は内側に正方形を描いたときも同様に成り立つことが知られており、このときはを満たす三角形の外側の点、つまりを満たす点となる。
更に、ボッテマの定理は任意の正多角形に一般化できる 。
三角形 に、それぞれ辺,を一辺とする正多角形を外側あるいは内側に描く。また正多角形の外接円上の頂点の対蹠点をそれぞれ,とする。この時、 の中点は の位置に依らない。
幾何学においてはカルノーの定理 (垂線)をボッテマの定理という場合もある。
関連
- ヴァン・オーベルの定理
- ナポレオンの定理
- キーペルト双曲線
参考文献
外部リンク
- Bottema's Theorem: What Is It?
- Wolfram Demonstrations Project – Bottema's Theorem
- GeoGebra Demonstrations Project - A Generalized Theorem - Equilateral Triangles
- GeoGebra Demonstrations Project - A Generalized Theorem - Regular Pentagons
![<高校数学講座>[C78] ド・モアブルの定理(3) 式の値 <複素数平面 8> YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/v4Pa6HXHoes/maxresdefault.jpg)